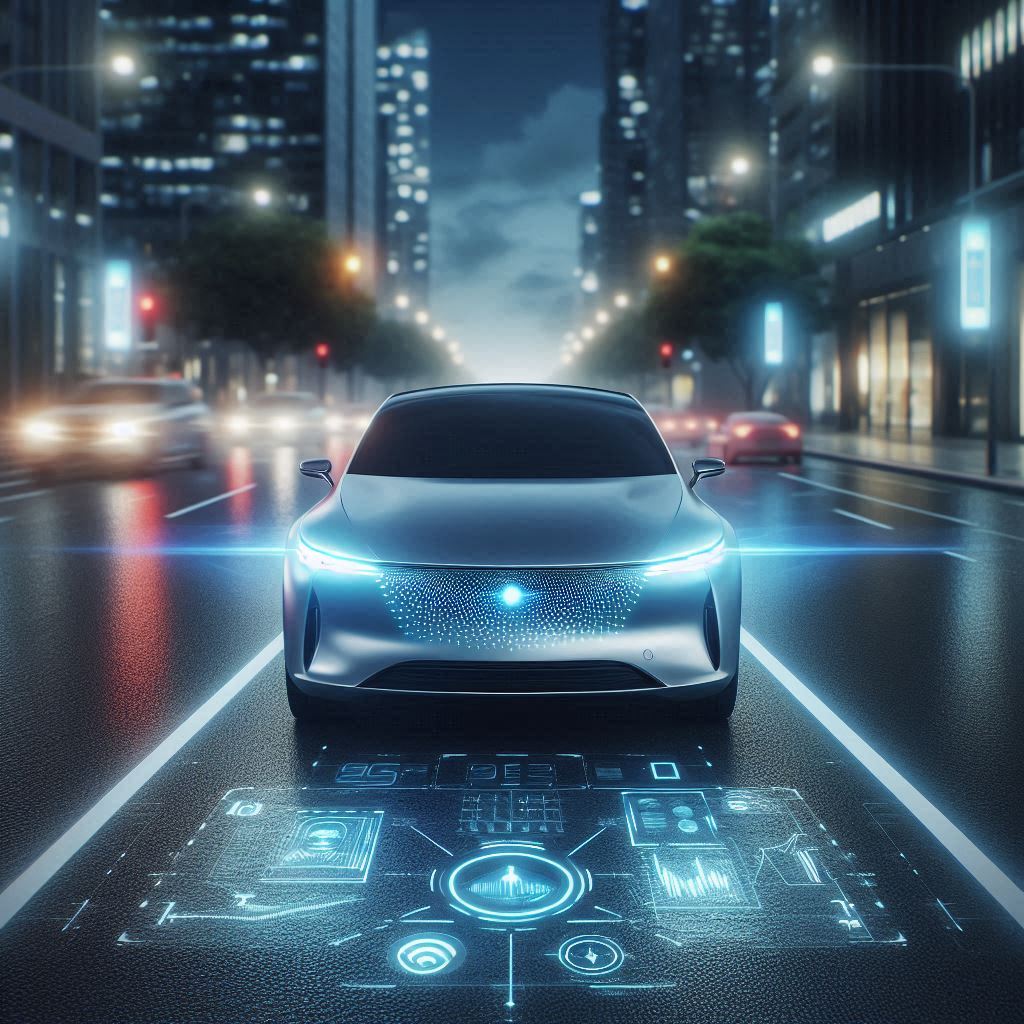
The concept of autonomous vehicles (AVs), once relegated to science fiction, is rapidly becoming a reality, poised to fundamentally reshape transportation systems, urban planning, and even our daily routines. Advancements in sensor technology, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and high-definition mapping are driving a revolution in mobility, with self-driving cars, trucks, buses, and delivery robots emerging from development labs and onto our streets. This transformation promises to bring about significant benefits, but also presents complex challenges that society must address.
The Technological Pillars of Autonomy:
Autonomous vehicles are complex systems reliant on a confluence of cutting-edge technologies:
- Advanced Sensor Systems: AVs utilize a suite of sensors, including LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors, to perceive their surroundings in 360 degrees. These sensors create a detailed 3D map of the environment, detecting objects, pedestrians, lane markings, and traffic signals.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI algorithms, particularly machine learning models, are the “brains” of autonomous vehicles. They process sensor data, interpret the environment, make driving decisions, and continuously learn and improve over time through data analysis and experience.
- High-Definition Mapping and Localization: AVs rely on highly detailed 3D maps to navigate and localize themselves within their environment with centimeter-level accuracy. These maps are constantly updated and refined through sensor data and cloud connectivity.
- Powerful Computing Platforms: Processing vast amounts of sensor data in real-time and executing complex AI algorithms requires powerful onboard computing platforms. These platforms are becoming increasingly energy-efficient and robust.
- Connectivity and Communication: AVs rely on reliable communication networks, including 5G, to connect to the cloud, receive map updates, communicate with other vehicles and infrastructure, and enable remote monitoring and control.
Transformative Applications Across Transportation and Logistics:
The impact of autonomous vehicles will be far-reaching, extending across various sectors:
- Personal Transportation: Self-driving cars promise to make personal transportation safer, more efficient, and more accessible. They can reduce accidents caused by human error, optimize traffic flow, and provide mobility solutions for the elderly and individuals with disabilities.
- Ride-Sharing and Mobility-as-a-Service: Autonomous fleets of ride-sharing vehicles can revolutionize urban transportation, offering on-demand mobility services at potentially lower costs and with greater efficiency.
- Logistics and Delivery: Self-driving trucks and delivery robots are poised to transform logistics and last-mile delivery. Autonomous trucks can improve efficiency and reduce costs in long-haul trucking, while delivery robots can automate last-mile deliveries in urban environments.
- Public Transportation: Autonomous buses and shuttles can enhance public transportation systems, providing more flexible and efficient routes, extending service hours, and potentially reducing operational costs.
- Specialized Applications: Autonomous vehicles are finding applications in specialized domains, such as mining, agriculture, construction, and warehousing, automating tasks in hazardous or repetitive environments.
Navigating the Road Ahead: Challenges and Societal Implications:
While the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles are significant, challenges and societal implications need careful consideration:
- Safety and Reliability: Ensuring the safety and reliability of AVs is paramount. Extensive testing, validation, and regulatory frameworks are crucial to build public trust and ensure safe deployment.
- Ethical and Legal Considerations: Autonomous vehicles raise complex ethical dilemmas in accident scenarios and require clear legal frameworks to address liability, insurance, and data privacy.
- Job Displacement: The automation of driving tasks could lead to job displacement for professional drivers in trucking, taxi services, and delivery industries, requiring workforce retraining and social safety nets.
- Infrastructure and Urban Planning: Cities need to adapt their infrastructure and urban planning to accommodate autonomous vehicles, including dedicated lanes, charging infrastructure, and smart traffic management systems.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: Securing AVs from cyberattacks and protecting the vast amounts of data they collect are critical concerns.
Driving Towards a Driverless Future:
Autonomous vehicles represent a transformative technology with the potential to reshape our world in profound ways. While challenges remain, the momentum behind AV development is undeniable. As technology matures, regulations evolve, and infrastructure adapts, we are steadily moving towards a future where autonomous vehicles play an increasingly prominent role in our transportation systems and urban landscapes, promising a safer, more efficient, and accessible future of mobility.